Safeguarding Healing: A Comprehensive Overview Of Medical Safety Products For Wound Care
Safeguarding Healing: A Comprehensive Overview of Medical Safety Products for Wound Care
Related Articles: Safeguarding Healing: A Comprehensive Overview of Medical Safety Products for Wound Care
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Safeguarding Healing: A Comprehensive Overview of Medical Safety Products for Wound Care. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Safeguarding Healing: A Comprehensive Overview of Medical Safety Products for Wound Care

Wound care, an essential aspect of healthcare, necessitates a multifaceted approach to ensure optimal healing outcomes. This involves not only the application of appropriate treatments but also the implementation of stringent safety measures to minimize the risk of complications and infections. Medical safety products play a pivotal role in this regard, providing a crucial layer of protection for both patients and healthcare professionals.
This comprehensive overview delves into the diverse array of medical safety products specifically designed for wound care. It will explore their individual functions, benefits, and applications, highlighting their significance in promoting safe and effective wound management.
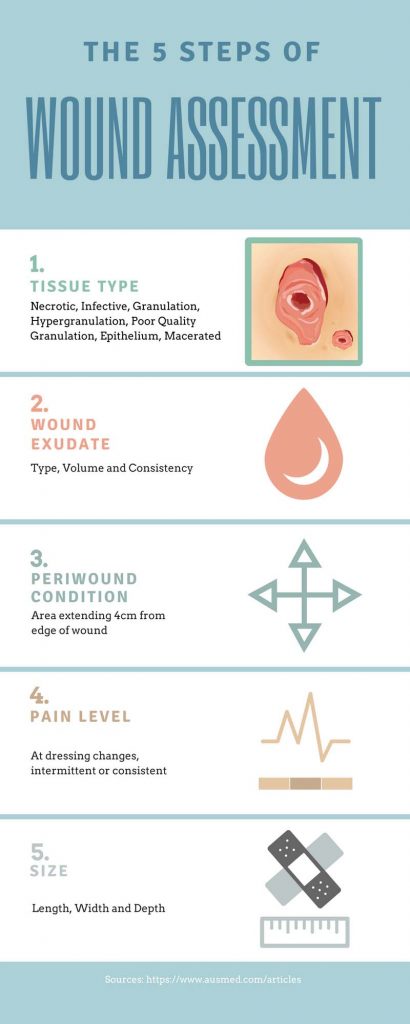
1. Protecting the Wound: Barriers and Dressings
a) Barriers:
The first line of defense against external contamination lies in the use of wound barriers. These products act as physical shields, preventing the ingress of microorganisms, debris, and other harmful substances into the wound environment.
- Wound Isolators: These devices, typically made of transparent, semi-permeable films, create a sterile, moisture-retentive environment over the wound. They facilitate visual monitoring of the wound while minimizing the risk of contamination.
- Fluid-Repellent Barriers: These barriers are designed to repel bodily fluids, such as blood and urine, preventing them from reaching the wound and potentially causing maceration or infection. They are particularly useful in situations where there is a high risk of fluid leakage, such as incontinent patients or those with draining wounds.
- Waterproof Barriers: These barriers provide a robust seal against water, preventing moisture from entering the wound site. They are crucial for patients who require frequent bathing or showering, ensuring that the wound remains protected from external contaminants.
b) Dressings:
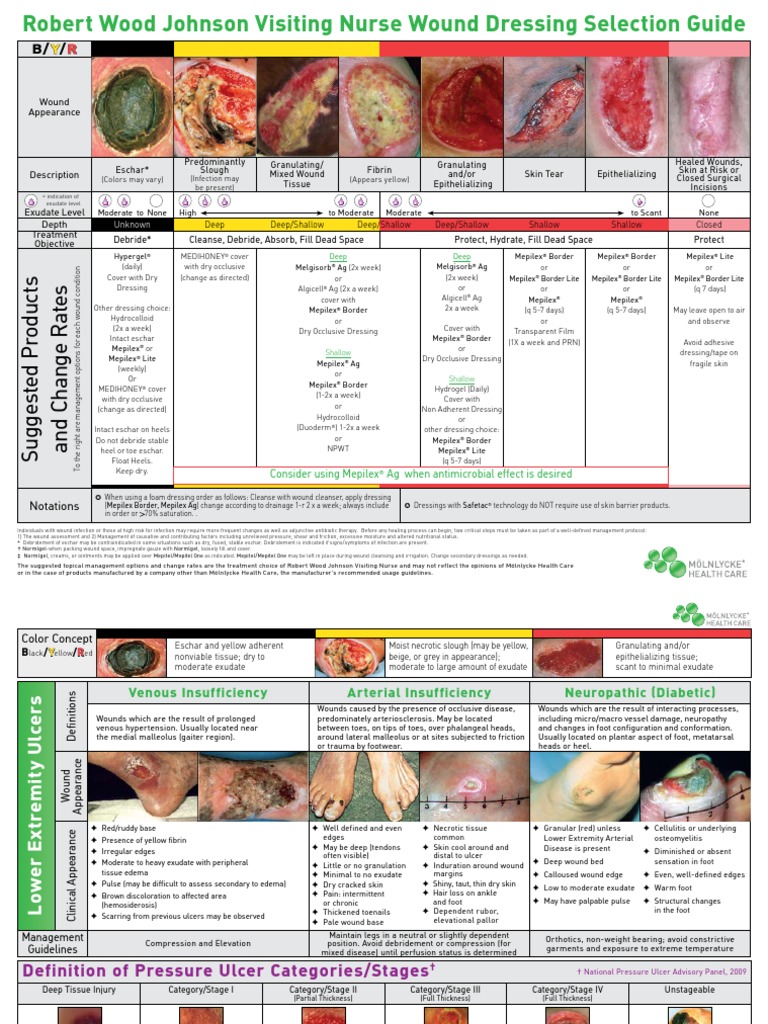
Wound dressings serve a multifaceted purpose, providing protection, promoting healing, and facilitating wound management. They are available in a wide range of materials and designs, each tailored to specific wound types and needs.
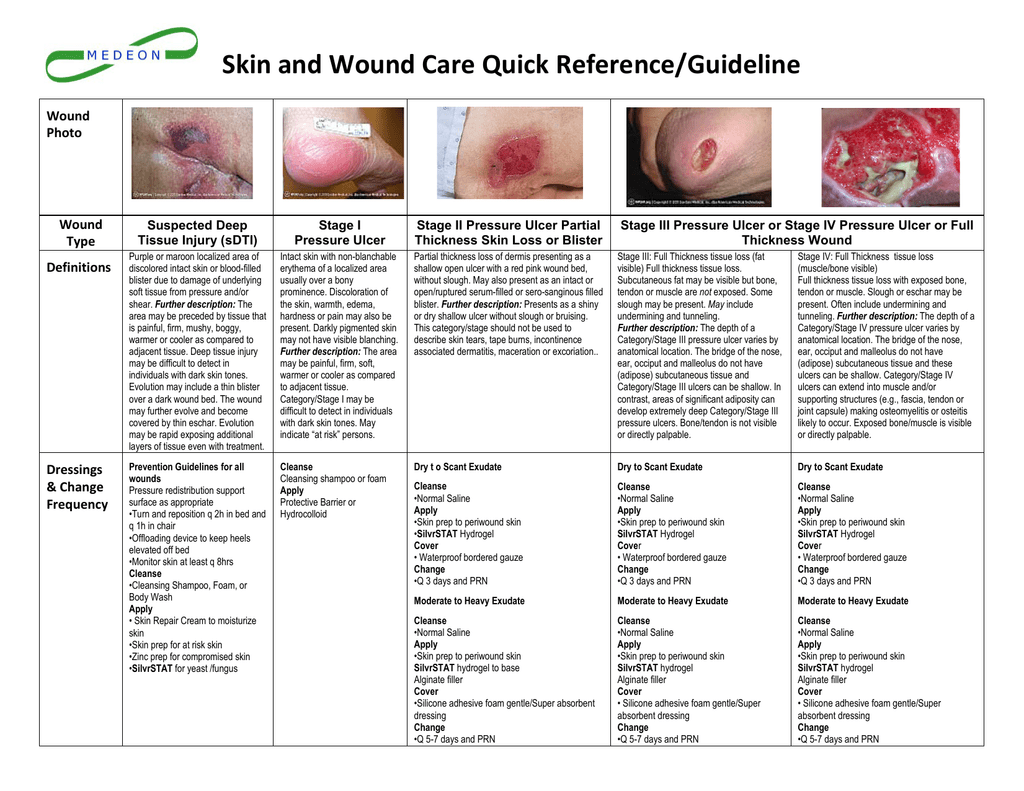
- Hydrocolloid Dressings: These dressings are composed of a gel-forming material that creates a moist environment, promoting autolytic debridement and epithelialization. They are effective for treating partial-thickness wounds, pressure ulcers, and burns.
- Hydrogel Dressings: These dressings are water-based gels that provide a soothing, hydrating environment for the wound. They are particularly beneficial for dry wounds and those with exposed tendons or bone.
- Foam Dressings: These dressings are made of absorbent foam that provides cushioning and protection to the wound. They are effective for managing moderate to heavy exudate, promoting wound healing and reducing pain.
- Alginate Dressings: These dressings are derived from seaweed and are highly absorbent, making them ideal for wounds with heavy exudate. They also possess hemostatic properties, aiding in controlling bleeding.
- Silver-Containing Dressings: These dressings incorporate silver ions, which possess potent antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing and treating wound infections, especially in cases of bacterial colonization.
2. Safeguarding the Caregiver: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Healthcare professionals are constantly exposed to potential hazards, including infectious agents, sharps injuries, and chemical exposures. Medical safety products play a crucial role in protecting them from these risks, ensuring their safety and well-being.
- Gloves: Gloves are an essential component of PPE, providing a barrier between the caregiver’s hands and potentially contaminated surfaces or bodily fluids. They are available in various materials, including latex, nitrile, and vinyl, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Masks: Masks prevent the inhalation of airborne particles, such as bacteria and viruses, protecting the caregiver from respiratory infections. Surgical masks are commonly used in wound care settings, providing a barrier against large droplets and splashes.
- Gowns: Gowns act as a protective barrier against splashes or contact with bodily fluids. They are typically worn during procedures involving wound care to minimize the risk of contamination.
- Eye Protection: Eye protection, such as goggles or face shields, is essential when working with potentially hazardous materials or procedures that could cause splashes or projectiles. They shield the eyes from contact with infectious agents or chemicals.
- Sharps Containers: These containers are designed to safely dispose of sharp medical waste, such as needles, scalpels, and lancets. They prevent accidental needle sticks and ensure proper disposal, minimizing the risk of infection.
3. Maintaining Cleanliness and Asepsis: Disinfection and Sterilization
Maintaining a sterile environment is paramount in wound care to prevent infection and promote healing. Medical safety products play a crucial role in achieving and maintaining aseptic conditions.
- Antiseptics: Antiseptics are solutions or preparations used to reduce the number of microorganisms on living tissue. They are typically applied to the skin around the wound to decrease the risk of contamination during dressing changes or procedures.
- Disinfectants: Disinfectants are used to kill microorganisms on inanimate objects, such as instruments, surfaces, and equipment. They are essential for maintaining a clean and sterile environment in wound care settings.
- Sterilization Equipment: Sterilization equipment, such as autoclaves and sterilizers, utilizes heat, steam, or chemicals to eliminate all microorganisms, including spores. This ensures that instruments and supplies are sterile before they are used on patients.
4. Facilitating Safe Wound Management: Devices and Accessories
Beyond the core safety products, various other devices and accessories contribute to safe and effective wound care.
- Wound Irrigation Systems: These systems provide a controlled means of irrigating wounds with sterile solutions, removing debris and promoting healing. They are particularly useful for cleaning deep wounds or those with heavy exudate.
- Wound Vacs: These devices, also known as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) systems, apply negative pressure to the wound bed, promoting drainage, reducing edema, and stimulating tissue growth.
- Wound Measurement Devices: These devices, such as rulers, calipers, and digital imaging systems, allow for accurate measurement of wound size and depth, enabling effective monitoring of healing progress.
- Skin Staplers: These devices provide a rapid and secure method for closing wounds, reducing the risk of infection and promoting healing.
- Wound Closure Strips: These strips, made of adhesive materials, provide a secure and comfortable means of closing small wounds, reducing the need for sutures.
5. The Importance of Education and Training
The effective use of medical safety products for wound care requires proper education and training. Healthcare professionals must be adequately trained in the selection, application, and disposal of these products to ensure their safe and effective use.
- Product-Specific Training: Manufacturers often provide training programs on the proper use and handling of their products, ensuring that healthcare professionals are fully informed about their specific characteristics and limitations.
- Continuing Education: Regular continuing education courses and workshops on wound care safety and best practices are crucial to keep healthcare professionals up-to-date on the latest advancements and guidelines.
FAQs regarding Medical Safety Products for Wound Care:
1. What are the most important considerations when choosing a wound dressing?
The choice of wound dressing should be guided by the type and severity of the wound, the amount of exudate, the patient’s individual needs, and the desired outcome. Factors such as the dressing’s ability to absorb exudate, promote healing, and prevent infection should be carefully considered.
2. How can I ensure that I am using PPE correctly?
Proper PPE use involves selecting the appropriate type of gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection based on the specific task and potential hazards. It also includes wearing the PPE correctly, ensuring a proper fit and avoiding any gaps or breaches in the protective barrier.
3. How do I dispose of sharps and other medical waste safely?
Sharps should always be disposed of in puncture-resistant sharps containers, which should be labeled appropriately and disposed of according to local regulations. Other medical waste, such as dressings and gloves, should be disposed of in designated waste bins, following infection control protocols.
4. What are the benefits of using wound irrigation systems?
Wound irrigation systems provide a controlled and effective means of cleaning wounds, removing debris, and reducing the risk of infection. They are particularly beneficial for deep wounds or those with heavy exudate.
5. How can I prevent sharps injuries?
Sharps injuries can be prevented by using appropriate safety devices, such as needleless systems, retractable needles, and safety syringes. It is also essential to handle sharps with care, avoiding unnecessary manipulation and ensuring proper disposal.
Tips for Using Medical Safety Products for Wound Care:
- Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for each product.
- Ensure that all products are properly stored and handled to maintain their sterility and effectiveness.
- Inspect all products before use, ensuring that they are intact and free from damage.
- Educate patients about the importance of proper wound care and the role of safety products.
- Maintain a clean and sterile environment for all wound care procedures.
- Dispose of all used safety products appropriately, following infection control protocols.
Conclusion:
Medical safety products play a vital role in promoting safe and effective wound care. By providing protection against contamination, minimizing the risk of infection, and safeguarding both patients and healthcare professionals, these products contribute significantly to optimal healing outcomes. Their proper selection, application, and disposal are essential for ensuring patient safety and achieving the best possible results in wound management. Continued education and training are crucial for maintaining a high standard of care and utilizing these products effectively to promote healing and minimize risks.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Safeguarding Healing: A Comprehensive Overview of Medical Safety Products for Wound Care. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Rise Of Natural Skincare In New Zealand: A Focus On Sustainability And Wellbeing
- A Comprehensive Guide To Popular Hair Care Products: Unveiling The Science Behind Healthy Hair
- Obagi Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Guide To Skin Care Innovation
- A Comprehensive Guide To Men’s Skin Care: Achieving Healthy, Vibrant Skin In Three Simple Steps
- The Rise Of Natural And Organic Skincare In The UK: A Comprehensive Guide
- The New York Skin Care Scene: A Tapestry Of Innovation And Tradition
- A Comprehensive Guide To Men’s Natural Skincare: Embracing A Holistic Approach To Healthy Skin
- Navigating The New Frontier Of Skincare: Unveiling The Innovations Of No7
Leave a Reply