A Comprehensive Guide To Medical Supplies For Wound Care
A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Supplies for Wound Care
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Supplies for Wound Care
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Supplies for Wound Care. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Supplies for Wound Care
Wounds, whether acute or chronic, are a common occurrence in healthcare settings and in everyday life. Effective wound care is essential for promoting healing, preventing infection, and minimizing complications. A wide range of medical supplies are available to facilitate this process, each designed to address specific aspects of wound management. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these supplies, highlighting their significance in optimizing patient outcomes.
I. Wound Care Products: An Essential Foundation for Healing
Wound care products encompass a diverse array of materials and technologies, each playing a critical role in facilitating the healing process. These products are categorized based on their intended use and the specific stage of wound healing.
A. Wound Cleansing and Irrigation
Maintaining a clean wound environment is paramount to preventing infection and promoting healing. This involves meticulous wound cleansing and irrigation, often utilizing specialized solutions.
- Normal Saline Solution (0.9% Sodium Chloride): This is the gold standard for wound irrigation, as it closely mimics the body’s natural fluids and is gentle on delicate tissues. It effectively removes debris and contaminants without disrupting the delicate healing process.
- Sterile Water: While less commonly used than saline, sterile water can be an effective irrigation solution in certain situations. It is important to note that prolonged use of sterile water can disrupt electrolyte balance in the wound bed.
- Antiseptic Solutions: These solutions, such as povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine, are used to kill bacteria and reduce the risk of infection. However, their use should be carefully considered, as prolonged exposure can damage healthy tissues and delay healing.
B. Wound Dressings: Protecting and Supporting Healing
Wound dressings serve as a protective barrier, providing a moist environment conducive to healing and minimizing the risk of infection. They are designed to absorb exudate, control moisture levels, and provide mechanical support.
- Gauze Dressings: These are the most common type of dressing, available in various sizes and forms. They are highly absorbent and can be used for a wide range of wounds. Non-adherent gauze dressings are particularly useful for wounds that are easily irritated.
- Hydrocolloid Dressings: These dressings create a moist environment, promoting autolytic debridement (the natural removal of dead tissue) and reducing the risk of infection. They are often used for chronic wounds, such as pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers.
- Hydrogel Dressings: Hydrogel dressings hydrate the wound bed, promoting granulation tissue formation and reducing pain. They are particularly effective for wounds with dry eschar (dead tissue).
- Foam Dressings: These dressings are highly absorbent and provide cushioning, making them ideal for wounds with moderate to high exudate levels. They can also be used to protect surrounding skin from maceration (softening of the skin).
- Transparent Film Dressings: These dressings allow for visual inspection of the wound while providing a moisture-retentive environment. They are often used for superficial wounds, such as abrasions and minor burns.
- Alginate Dressings: Alginate dressings are highly absorbent and form a gel-like substance that helps control exudate and promote healing. They are particularly effective for wounds with heavy exudate, such as venous ulcers.
- Silver-Containing Dressings: These dressings contain silver ions, which have antimicrobial properties. They are often used for infected wounds or wounds at risk of infection.
C. Wound Closure Products: Facilitating Healing and Minimizing Scarring
Wound closure products are used to approximate wound edges, promoting healing and minimizing scarring.
- Sutures: Sutures are fine threads used to close wounds. They come in various materials, including nylon, silk, and absorbable materials. The choice of suture material depends on the location and nature of the wound.
- Staples: Staples are metal fasteners used to close wounds, particularly in areas with a high risk of tension, such as scalp wounds.
- Skin Adhesives: Skin adhesives are liquid or gel-like products that adhere to the skin, closing wounds without the need for sutures or staples. They are often used for superficial wounds, such as lacerations and abrasions.
- Wound Closure Strips: These strips are adhesive strips applied to the skin, providing support and promoting wound closure. They are often used for superficial wounds, such as lacerations and abrasions.
II. The Importance of Medical Supplies in Wound Care
The use of appropriate medical supplies is crucial in wound care for several reasons:
- Promoting Healing: Wound care products create an optimal environment for wound healing, promoting tissue regeneration and reducing the risk of infection.
- Preventing Infection: Proper wound cleansing and the use of antimicrobial dressings help control bacterial growth and minimize the risk of infection.
- Managing Exudate: Absorbent dressings effectively control wound exudate, preventing maceration and promoting healing.
- Providing Comfort: Certain dressings provide cushioning and protect the wound from external irritation, enhancing patient comfort.
- Facilitating Wound Closure: Wound closure products effectively approximate wound edges, promoting healing and minimizing scarring.
- Improving Patient Outcomes: The use of appropriate medical supplies contributes to faster healing times, reduced complications, and improved patient satisfaction.
III. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Medical Supplies for Wound Care
1. What are the signs of a wound infection?
Signs of a wound infection include redness, swelling, pain, warmth, pus, foul odor, and fever.
2. How often should I change my wound dressing?
The frequency of dressing changes depends on the type of dressing, the amount of exudate, and the wound’s condition. It is essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
3. Can I use over-the-counter products for wound care?
While some over-the-counter products may be suitable for minor wounds, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider for guidance on the appropriate products and procedures for your specific wound.
4. What are the potential complications of wound care?
Potential complications of wound care include infection, delayed healing, scarring, and chronic wounds.
5. How can I prevent wound infections?
To prevent wound infections, maintain a clean wound environment, use appropriate dressings, and follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully.
IV. Tips for Effective Wound Care at Home
- Keep the wound clean: Gently cleanse the wound with normal saline solution or sterile water.
- Apply appropriate dressing: Choose a dressing that is appropriate for the type and size of the wound, and change it regularly as instructed.
- Monitor the wound: Observe the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, warmth, pus, foul odor, and fever.
- Keep the wound dry: Avoid soaking the wound in water or using harsh soaps.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions: Adhere to your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding wound care and medication.
V. Conclusion
Medical supplies for wound care play a vital role in promoting healing, preventing infection, and minimizing complications. By understanding the different types of products and their applications, healthcare professionals and individuals can effectively manage wounds and optimize patient outcomes. The use of these supplies is essential for achieving optimal healing and preventing the development of chronic wounds, ultimately contributing to a higher quality of life for patients.





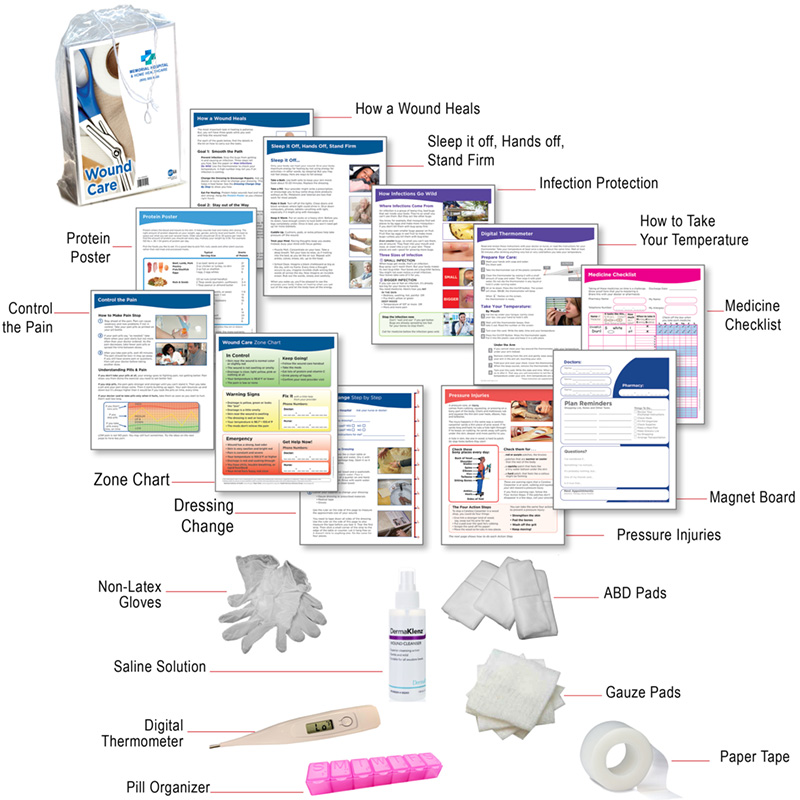

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Supplies for Wound Care. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Rise Of Natural Skincare In New Zealand: A Focus On Sustainability And Wellbeing
- A Comprehensive Guide To Popular Hair Care Products: Unveiling The Science Behind Healthy Hair
- Obagi Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Guide To Skin Care Innovation
- A Comprehensive Guide To Men’s Skin Care: Achieving Healthy, Vibrant Skin In Three Simple Steps
- The Rise Of Natural And Organic Skincare In The UK: A Comprehensive Guide
- The New York Skin Care Scene: A Tapestry Of Innovation And Tradition
- A Comprehensive Guide To Men’s Natural Skincare: Embracing A Holistic Approach To Healthy Skin
- Navigating The New Frontier Of Skincare: Unveiling The Innovations Of No7

Leave a Reply